Table of Contents
ToggleKolhapur
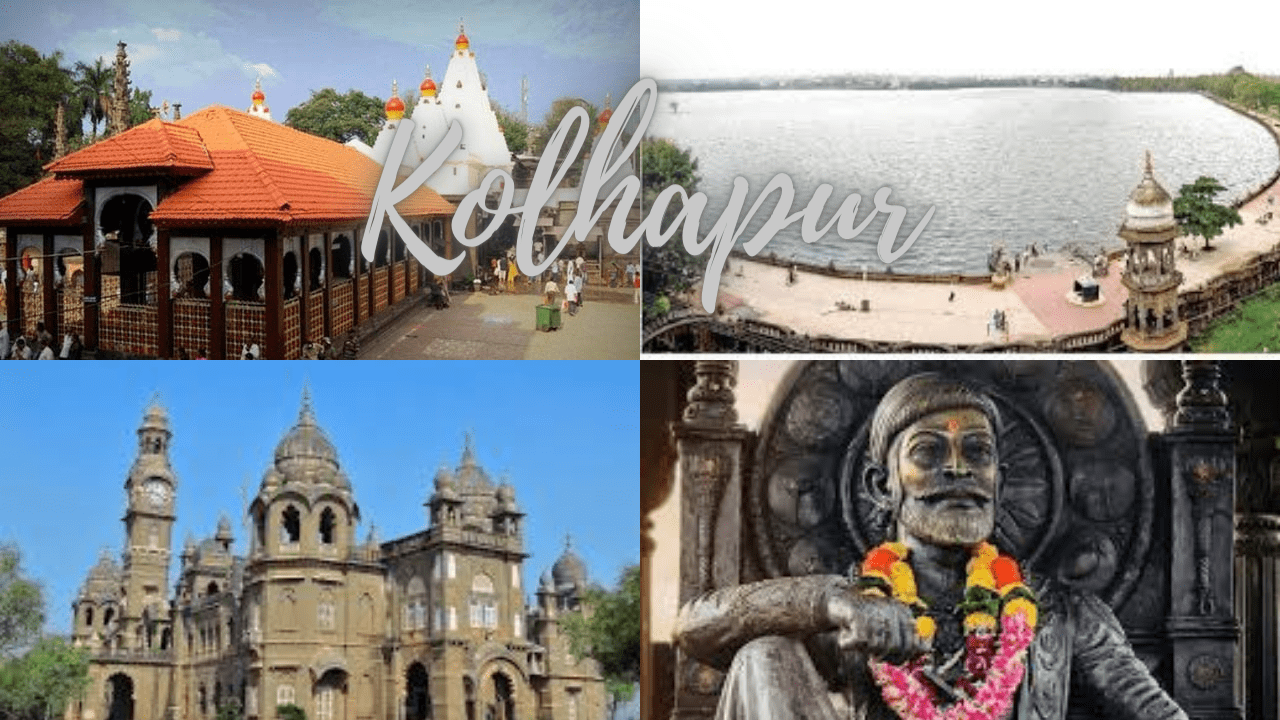
History of Kolhapur: Kolhapur is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarter of the Kolhapur district. Kolhapur is known as Dakshin Kashi or Kashi of the South because of its spiritual history and the antiquity of its shrine Mahalaxmi, better known as Ambabai. The region is known for the production of the famous hand-crafted and braided leather slippers called Kolhapuri chappal, which received the Geographical Indication designation in 2019.In Hindu mythology, Kolhapur is referred to as Karvir.
Before India became independent in 1947, Kolhapur was a princely state under the Bhosale Chhatrapati of the Maratha Empire. Kolhapur is an important center for the Marathi film industry.
Etymology of Kolhapur
Kolhapur is named after Kolhasur, a demon in Hindu History. According to History, the demon Kolhasur renounced asceticism after his sons were killed by God for harassing people, and prayed to Mahalakshmi that she would leave the area to him for a hundred years. He committed numerous crimes until the goddess returned after the hundred years were over and killed him for his sins. The dying wish of Kolhasur was to name the place after him, which was granted and the place was named Kolhapur. Kolha stands for Kolhasur and pur, a Sanskrit word, means “city”.
History
Medieval era
The Shilahara family founded a dynasty at Kolhapur about the time of the downfall of the Rashtrakuta Empire, that ruled over southern Maharashtra including the modern districts of Satara, Kolhapur and Belagavi (Karnataka). Their family deity was the goddess Ambabai, whose blessing they claimed to have secured in their copperplate grants (Mahalakshmi-labdha-vara-prasada).
Like their relatives of the northern branch of Konkan, the Shilaharas of Kolhapur claimed to be of the lineage of Vidyadhara Jimutavahana, a Jain scholar. Their banner featured a golden Garuda. One of the many titles used by the Shilaharas was Tagarapuravaradhisvara, supreme sovereign ruler of Tagara.
The first capital of the Shilaharas was probably at Karad during the reign of Jatiga II, as known from their copper plate grant of Miraj and ‘Vikramankadevacharita’ of Bilhana.
Hence, they are referred to sometimes as the Shilaharas of Karad. Later, although the capital was shifted to Kolhapur, some of their grants mention Valavada and the hill fort of Pranalaka or Padmanala (Panhala) as the places of royal residence. Karhad retained its significance during the Shilahara period. This branch rose to power in the latter part of the Rashtrakuta rule and unlike the kings of the other two branches, this branch does not allude to the genealogy of the Rashtrakutas even in their early grants.
They acknowledged the suzerainty of the later Chalukya dynasty for some time. They had used Kannada as an official language as can be seen from their inscriptions. The branch held southern Maharashtra from circa 940 to 1220.
From 940 to 1212 CE, Kolhapur was the centre of power of the Shilahara dynasty. An inscription at Terdal states that the king Gonka (1020 – 1050 CE) was bitten by a snake then healed by a Jain monk. Gonka then built a temple to Lord Neminath, the twenty-second Jain tirthankara (enlightened being). From this era, Jain temples in and around Kolhapur are called Gonka-Jinalaya.
Around 1055 CE, during the reign of Bhoja I (Shilahara dynasty), a dynamic Acharya (spiritual guide) named Maghanandi (Kolapuriya) founded a religious institute at the Rupanarayana Jain temple (basadi). Maghanandi is also known as Siddhanta-Chakravarti, meaning the great master of the scriptures. Kings and nobles of the Shilahara dynasty such as Gandaraditya I, who succeeded Bhoja I, were disciples of Maghanandi.
Kolhapur was the site of intense confrontation between the Western Chalukya Empire and Rajadhiraja Chola and his younger brother Rajendra Chola II of the Chola empire. In 1052 CE, following the Battle of Koppam, the victor, Rajendra Chola II, marched on to Kolhapur and erected a jayastambha (victory pillar).
Between 1109 and 1178 CE, the Kopeshwar temple to Lord Shiva was built by Shilahara kings, Gandaraditya I, Vijayaditya, and Bhoja II in Khidrapur, Kolhapur.
Kolhapur State
The state of Kolhapur was established by Tarabai in 1707 in the midst of a succession dispute over the Maratha crown. The Maratha throne was then occupied by descendants of Tarabai. One of the prominent Kings was Rajarshi Shahu Maharaj (Shahu of Kolhapur). In his reign, he promoted free education to people of all castes and fought against untouchability. The state was annexed by the British in the 19th century. After India’s independence in 1947, the Maharaja of Kolhapur acceded to the Dominion of India on 14 August 1947 and merged with Bombay State on 1 March 1949. Kolhapur is sometimes found spelled as Colapore.
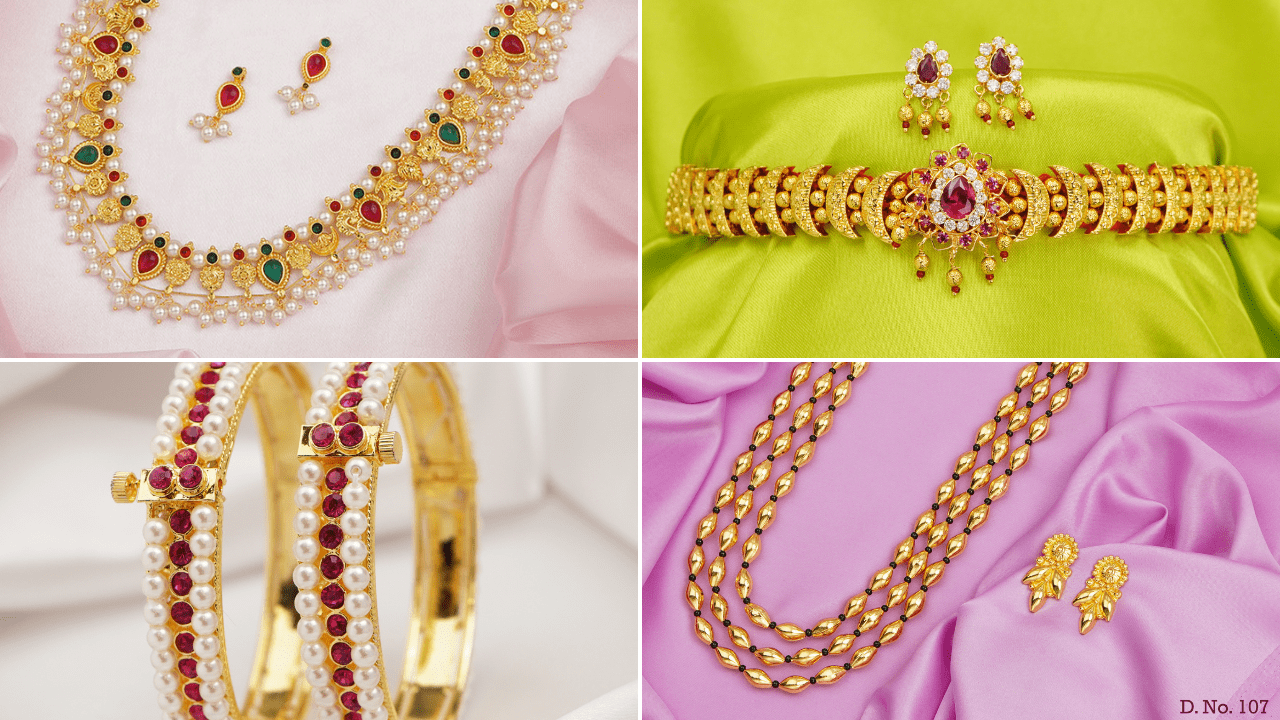
Kolhapuri Jewellery
Medieval era
The Shilahara family founded a dynasty at Kolhapur about the time of the downfall of the Rashtrakuta Empire, that ruled over southern Maharashtra including the modern districts of Satara, Kolhapur and Belagavi (Karnataka). Their family deity was the goddess Ambabai, whose blessing they claimed to have secured in their copperplate grants (Mahalakshmi-labdha-vara-prasada).
Like their relatives of the northern branch of Konkan, the Shilaharas of Kolhapur claimed to be of the lineage of Vidyadhara Jimutavahana, a Jain scholar. Their banner featured a golden Garuda. One of the many titles used by the Shilaharas was Tagarapuravaradhisvara, supreme sovereign ruler of Tagara.
The first capital of the Shilaharas was probably at Karad during the reign of Jatiga II, as known from their copper plate grant of Miraj and ‘Vikramankadevacharita’ of Bilhana.
Hence, they are referred to sometimes as the Shilaharas of Karad. Later, although the capital was shifted to Kolhapur, some of their grants mention Valavada and the hill fort of Pranalaka or Padmanala (Panhala) as the places of royal residence. Karhad retained its significance during the Shilahara period. This branch rose to power in the latter part of the Rashtrakuta rule and unlike the kings of the other two branches, this branch does not allude to the genealogy of the Rashtrakutas even in their early grants.
They acknowledged the suzerainty of the later Chalukya dynasty for some time. They had used Kannada as an official language as can be seen from their inscriptions. The branch held southern Maharashtra from circa 940 to 1220.
From 940 to 1212 CE, Kolhapur was the centre of power of the Shilahara dynasty. An inscription at Terdal states that the king Gonka (1020 – 1050 CE) was bitten by a snake then healed by a Jain monk. Gonka then built a temple to Lord Neminath, the twenty-second Jain tirthankara (enlightened being). From this era, Jain temples in and around Kolhapur are called Gonka-Jinalaya.
Around 1055 CE, during the reign of Bhoja I (Shilahara dynasty), a dynamic Acharya (spiritual guide) named Maghanandi (Kolapuriya) founded a religious institute at the Rupanarayana Jain temple (basadi). Maghanandi is also known as Siddhanta-Chakravarti, meaning the great master of the scriptures. Kings and nobles of the Shilahara dynasty such as Gandaraditya I, who succeeded Bhoja I, were disciples of Maghanandi.
Kolhapur was the site of intense confrontation between the Western Chalukya Empire and Rajadhiraja Chola and his younger brother Rajendra Chola II of the Chola empire. In 1052 CE, following the Battle of Koppam, the victor, Rajendra Chola II, marched on to Kolhapur and erected a jayastambha (victory pillar).
Between 1109 and 1178 CE, the Kopeshwar temple to Lord Shiva was built by Shilahara kings, Gandaraditya I, Vijayaditya, and Bhoja II in Khidrapur, Kolhapur.
Kolhapur State
The state of Kolhapur was established by Tarabai in 1707 in the midst of a succession dispute over the Maratha crown. The Maratha throne was then occupied by descendants of Tarabai. One of the prominent Kings was Rajarshi Shahu Maharaj (Shahu of Kolhapur). In his reign, he promoted free education to people of all castes and fought against untouchability. The state was annexed by the British in the 19th century. After India’s independence in 1947, the Maharaja of Kolhapur acceded to the Dominion of India on 14 August 1947 and merged with Bombay State on 1 March 1949. Kolhapur is sometimes found spelled as Colapore.